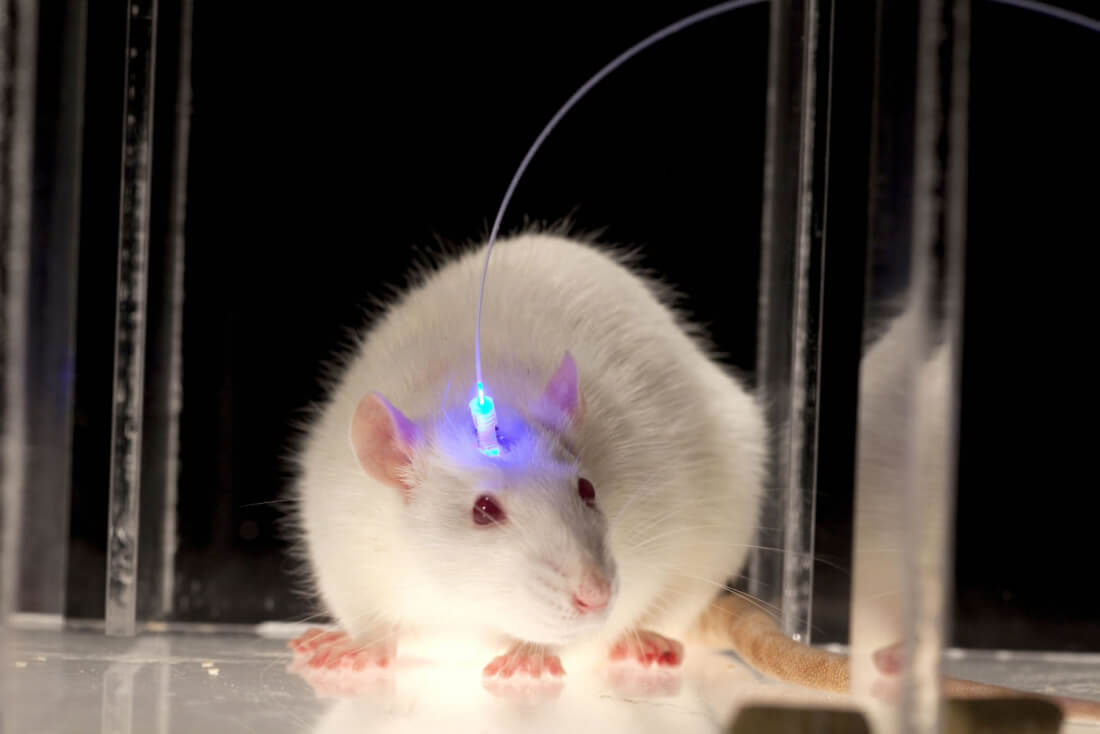
Our brains communicate with electrical and novapatra sex videochemical signaling, but scientists have discovered that light stimulation could hold potential keys to manipulating neuronal communication pathways that influence motor control, sensory perception, memory, neurochemical production and mood – or cellular virtual reality, as a report from the Journal of Cell Biology describes it.
With the roll out of the White House's $300 million BRAIN Initiative in 2013, interest in uncovering the secrets of the human brain has accelerated and now includes many government agencies, public/private partnerships and universities.
Dating back to at least 1971, optogenetic research has matured enough to gain the attention of organizations such as the NIH, DARPA and IARPA, who are exploring the role that light-sensitive cells could soon play in fields surrounding neurobiological, including physical and mental health, human-machine interfacing, and advancing artificial intelligence through reverse brain engineering.
Current optogenetic experiments rely on extracting "opsins" (light-sensitive proteins) from plants which can be introduced to mammals by methods including injection and infection via adenovirus.
Once delivered into an organism, opsins can be expressed in eye, brain or skin cells, allowing their light-sensitivity to be remotely activated or silenced with timed pulses of light in different color wavelengths across the light spectrum that can target multiple bodily systems and cause a variety of biological effects.
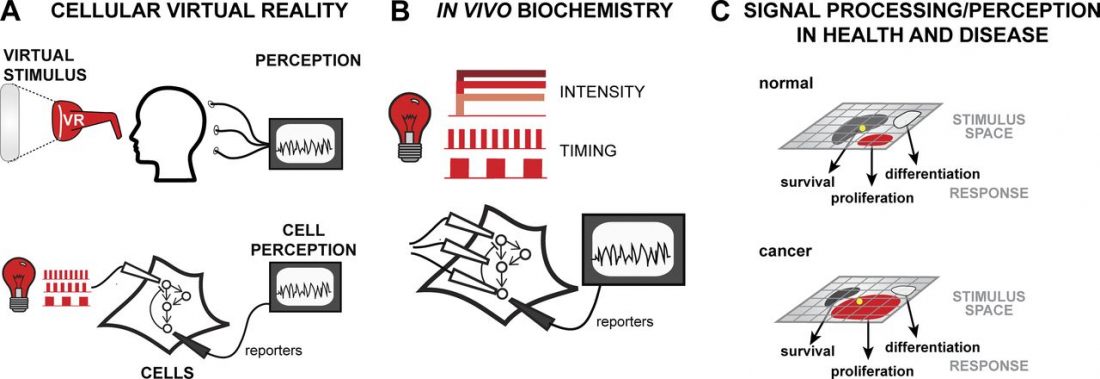
Researchers have suggested however that introducing opsins into an organism may not be a long-term requirement as methods are sought for using optogenetics on mammalian cells that respond naturally to light, such as those in the human retina.
As part of the BRAIN Initiative, scientists have been working on neuronal barcoding and completing a detailed online brain atlas for researchers. This is hoped to eventually provide a detailed circuit diagram of every neuron and synapse in the brain, which would allow various neuronal patterns to be identified so they can be triggered for the desired effect.
If targeted precisely enough with the appropriate light, it's thought that optogenetics could be used by manipulating neural circuits involved with pain, fear, reward, wakefulness and social behaviors. In one Yale study, for example, mice were infected with a virus which made their neurons sensitive to blue light. Scientists then used that light pathway to activate predatory behavior.
"...The researchers used a tiny optic fibre to shine a blue laser on the amygdala. This prompted the animals to tense their jaw and neck muscles... 'It's not just physiological, it's hunting, biting, releasing and eating. Those are motor sequences that require a lot of information...' [said an MIT neuroscientist]"
In 2015, optogenetics was combined with CRISPR to develop a set of photoactivatable tools that enable the editing of an organism's genome through the external use of light. Said tools can control the location, timing and reversibility of the genome editing process, whether that be activating, repressing or modifying a gene.
Optogenetics is also mentioned as an integral feature of the DARPA-funded Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program, a joint effort between six teams who are aiming to create an implantable neural interface over the next four years that is capable of high resolution brain-to-machine communication. Such advancements, for instance, could facilitate the development of mind-controlled prosthetics featuring touch sensation like the DARPA-backed 'Luke' arm (previously known as the 'Deka' arm).
In the past, DARPA has looked to optogenetic memory manipulation techniques for treating veterans with traumatic brain injury and/or PTSD through memory restoration or deletion.
More recently, during a November 2017 mental health conference with 30,000 attendees in Washington D.C., optogenetics was noted for the impact it's having on the ability to study the brain. According NPR science correspondent Jon Hamilton, the technology has allowed aspects of human mental health disorders to be reproduced in animals, aiding the mapping of neuronal circuits involved with issues such as depression.
Companies interested in the application of optogenetic technologies have begun emerging over the last decade, particularly since the FDA approved the technology in 2015 for use in treating an eye disorder known as "retinitis pigmentosa."
The approval prompted a clinical trial and optogenetic developments have since been used to restore partial vision in patients who were described as being "profoundly blind." Chronic pain management, epilepsy and Parkinson's are among many health issues that researchers are experimenting with addressing through optogenetics.
The technology is also contributing to other areas of research such as "sonogenetics," which uses low-pressure ultrasound to activate ultrasonically sensitized neurons. This is another area of interest for DARPA, which has funded Columbia University's endeavor to stimulate neurons using ultrasound and believes it could eventually lead to a magnetic version of the technology called "magnetogenetics."
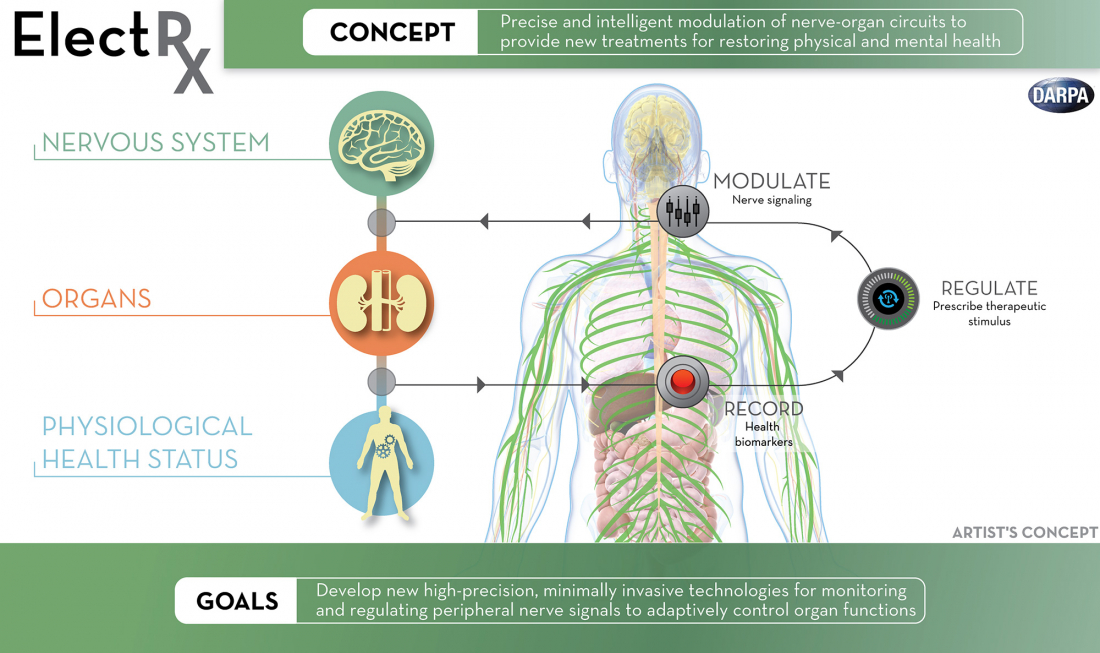
To investigate the therapeutic use of optogenetics, acoustics and electromagnetic fields, DARPA launched the ElectRX (Electrical Prescription) program in 2015, which is capable of stimulating, modulating and monitoring the body's peripheral nervous system. The research agency is also exploring how artificial intelligence could be used in closed-loop brain implants, such as the ability to detect patterns associated with mood disorders.
With enough progress, it's believed that optogenetics and its surrounding bodies of research may open the door to real-time brain mapping and biofeedback technologies, which could be used to treat all manner of ailments on the fly through closed-loop neuromodulation signals coming to and from an implanted device, ultimately eliminating the need for pharmaceuticals.
 Cold Tofu Named Nisei Week Parade Marshal
Cold Tofu Named Nisei Week Parade Marshal
 What's new to streaming this week? (Dec. 06, 2024)
What's new to streaming this week? (Dec. 06, 2024)
 NYT mini crossword answers for December 6
NYT mini crossword answers for December 6
 Elon Musk fails bid to restore $55.8 billion Tesla pay package
Elon Musk fails bid to restore $55.8 billion Tesla pay package
 San Diego’s Largest Film Festival Announces 140+ Film Line
San Diego’s Largest Film Festival Announces 140+ Film Line
 Wordle today: The answer and hints for December 6
Wordle today: The answer and hints for December 6
 OpenAI one step closer to the Pentagon thanks to partnership with defense startup
OpenAI one step closer to the Pentagon thanks to partnership with defense startup
 Best AirPods deal: Save $40 on Apple AirPods 4
Best AirPods deal: Save $40 on Apple AirPods 4
 OCBC Troop 578 Recognizes 5 New Eagle Scouts
OCBC Troop 578 Recognizes 5 New Eagle Scouts
 Best robot vacuum deals: The 4 most advanced Roombas are on sale at record
Best robot vacuum deals: The 4 most advanced Roombas are on sale at record
 blameF on becoming IGL: "I know my individual level is going to take a hit"
blameF on becoming IGL: "I know my individual level is going to take a hit"
 NYT Strands hints, answers for December 5
NYT Strands hints, answers for December 5
 Cheating has become the ultimate crime online
Cheating has become the ultimate crime online
 Google Search AI Overviews at 6 months: Is the feature getting better?
Google Search AI Overviews at 6 months: Is the feature getting better?
 fnatic defeat B8 to qualify for BLAST.tv Paris Major
fnatic defeat B8 to qualify for BLAST.tv Paris Major
 Stephen King trolls Elon Musk once again over Twitter's name change
Stephen King trolls Elon Musk once again over Twitter's name change
 Webb telescope exposes secrets of a famous cosmic metropolis
Webb telescope exposes secrets of a famous cosmic metropolis
 Best TV deal: Save $150 on the TCL Q5 65
Best TV deal: Save $150 on the TCL Q5 65
 Japanese Bands’ Continued Dedication to Giving
Japanese Bands’ Continued Dedication to Giving
 At 2 a.m., an unexpected event led to a surprise planet discovery
At 2 a.m., an unexpected event led to a surprise planet discovery
Molly SussmanXbox One: Entertainment Hub First, Gaming Console SecondSteelers vs. Giants 2024 livestream: How to watch NFL for freeBest home goods deal: Spend $80 on qualifying P&G items and get a $20 Amazon creditMars scientists spent 6 years making the most detailed image of the planetElection 2024: The truth about voting machine securityBoy AfraidNYT Connections hints and answers for October 27: Tips to solve 'Connections' #504.Hong Kong Open 2024 livestream: Watch live tennis for freeWebb telescope sees galaxy collision brighter than 1 trillion suns How to backup iPhone Bose headphone deal: Get the Bose noise Windows 10 will start pushing users to use Microsoft accounts. How to turn it off. Best TV deal: Get a 32 Earth will look wildly different in millions of years. Take a look. Twitter/X might charge all new users a 'small fee' before they can post, like, and reply 'GTA 6' publisher lays off 5 percent of workforce, cancels games iPad Air 2024: No OLED, but it’s tipped to get this big display upgrade How to log out of Netflix on Apple TV, Roku, Fire, and more Best Fire tablet deal: Get the Amazon Fire HD 8 Kids Pro tablet for just $99.99 at Amazon
0.2226s , 14319.0625 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【novapatra sex video】Optogenetics: A Virtual Reality System for Controlling Living Cells,Feature Flash